All About Radiation Inversion
Radiation fog is a very common type of fog throughout the united states. It is most prevalent during the fall and winter.
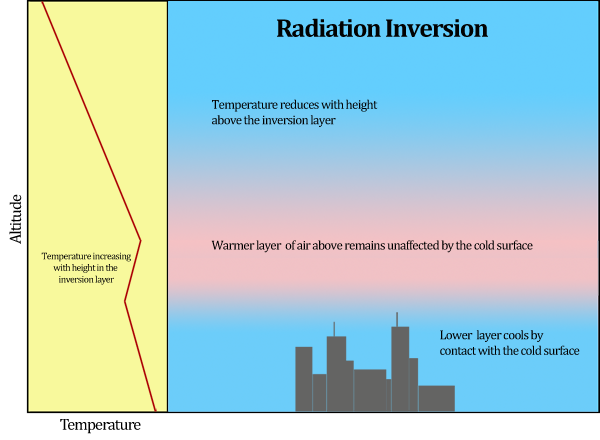 Recognising A Temperature Inversion
Recognising A Temperature Inversion
www.brisbanehotairballooning.com.au
This lecture aims to explain why temperature increases with height.

All about radiation inversion. Upsc mains 2013 question. Looking for radiational inversion. A common type of inversion is the radiational cooling inversion in which overnight the earths air near the surface cools by ground surface longwave radiation emission.
What do you understand by phenomenon of temperature inversion in meteorology. A population inversion n 2 n 1 has thus been achieved between level 1 and 2 and optical amplification at the frequency n 21 can be obtained. Adiabatic lapse rate latent heat of condensation temperature inversion temperature inversion is a reversal of the normal behavior of temperature in the troposphere in which a layer of cool air at the surface.
Usually occurs on cold winter nights explanation of radiational inversion. Because at least half the population of atoms must be excited from the ground state to obtain a population inversion the laser medium must be very strongly pumped. Types of temperature inversions inversion surface air frontal upper air 6.
Manishika jain explains the concept of temperature inversion like surface inversion ground inversion and frontal inversion. Radiation inversions are the most common type of inversion but there exists other inversions like advection and subsidence inversions as well. An inversion is also produced whenever radiation from the surface of the earth exceeds the amount of radiation received from the sun which commonly occurs at night or during the winter when the angle of the sun is very low in the sky.
An inversion at the land surface resulting from rapid radiational cooling of lower air. Find out information about radiational inversion. Winter temperature inversions play a significant role in the winter pollution episodes in nordic urban sites.
Fogs are prone to form within radiation inversion layers. It forms overnight as the air near the ground cools and stabilizes. This effect is virtually confined to land regions as the ocean retains heat far longer.
Surface inversion inversion near the surface is of very short duration because the solar radiation heats the surface during day time warms up the pre existing cold air near the surface which soon disappears at night and hence the temperature inversion also disappears. How do inversions impact air quality. The top of an inversion may experience a sudden increase in wind speed and or direction and turbulence.
When this cooling causes the air to reach saturation fog will form. Fog will first form at or near the. An inversion layer is a layer of stability since cold air under warm air is a stable situation.
The optimum conditions for a radiation inversion is a dry clear and long night. W ithin the inversion layer visibility may be reduced by trapped particles of smoke and dust. How does it affect weather and habitants of the place.
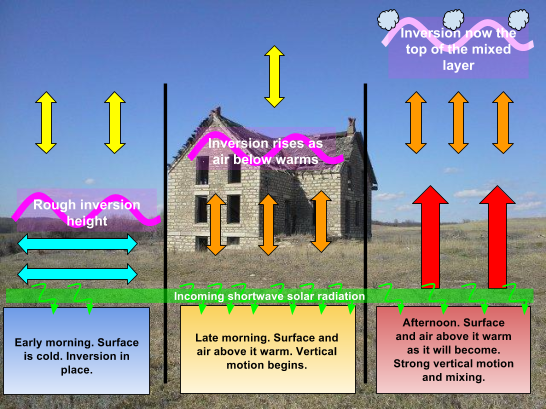 Kansas Mesonet Inversions
Kansas Mesonet Inversions
mesonet.k-state.edu
 Air Pollution Control L 14
Air Pollution Control L 14
www.slideshare.net
 Remote Sensing Free Full Text Inversion Of The Fraction Of
Remote Sensing Free Full Text Inversion Of The Fraction Of
www.mdpi.com
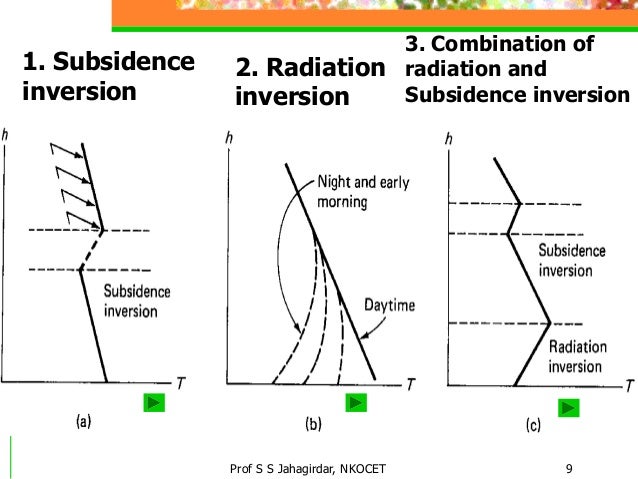 Air Pollution Control L 14
Air Pollution Control L 14
www.slideshare.net
 Surface Inversions Sprayers 101
Surface Inversions Sprayers 101
sprayers101.com
Subsidence Inversions
www-das.uwyo.edu
 Radiation Inversions Youtube
Radiation Inversions Youtube
www.youtube.com
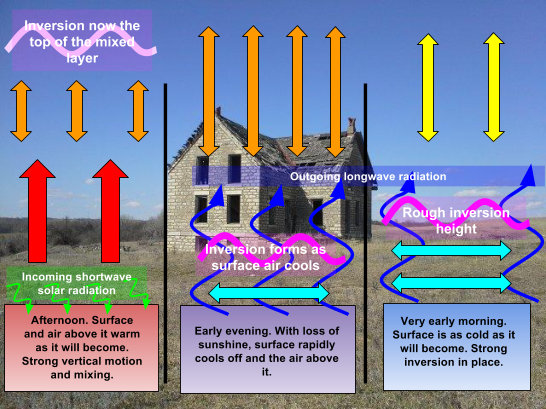 Kansas Mesonet Inversions
Kansas Mesonet Inversions
mesonet.k-state.edu

0 Response to "All About Radiation Inversion"
Post a Comment