All About Scatter Radiation
The main difference between the effects of single and multiple scattering is that single. Scatter radiation is a type of secondary radiation that occurs when the useful beam intercepts any object causing some x rays to be scattered.
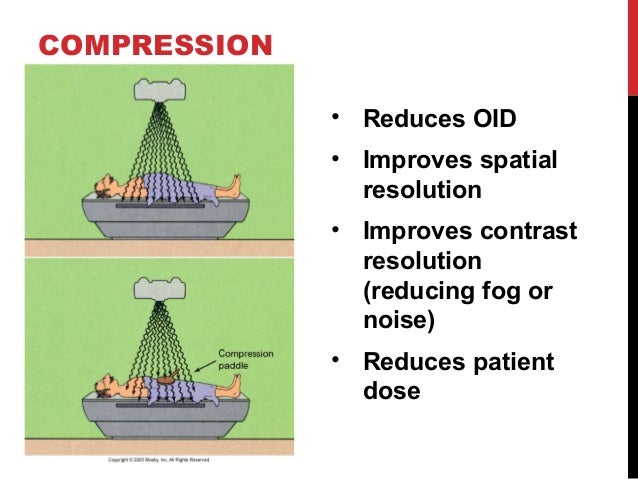 Rad 206 P11 Fundamentals Of Imaging Control Of Scatter Radiation
Rad 206 P11 Fundamentals Of Imaging Control Of Scatter Radiation
www.slideshare.net
Fortunately the minimal amounts of radiation absorbed via these sources pose no real threat to our wellbeing.

All about scatter radiation. For those who work in the diagnostic and therapeutic fields or for patients whose medical conditions require frequent. Scatter radiation introduced in chapter 2 is produced as a result of the attenuation of the x ray beam by matterthis chapter explores the production of scatter radiation and the factors that influence its formation. In such cases radiation may scatter many times in what is known as multiple scattering.
For example during x ray mammography very small amounts of radiation may be scattered to areas away from the breast such. Scatter radiation is a secondary radiation produced when an x ray interact with the patient and the energy is not enough for an x ray to reach the ir. Nci dictionary of cancer terms.
When radiation is only scattered by one localized scattering center this is called single scattering. All humans experience radiation exposure daily due to sunlight radio and microwaves our smartphones and even the foods we eat. It is very common that scattering centers are grouped together.
Selective absorption of scattered radiation by a grid. During an x ray or fluoroscopic exam the patient is the most significant source of scatter radiation. The ideal grid would absorb all scattered radiation and allow all primary x rays to penetrate to the receptor.
Therefore the radiographer must act to minimize the amount of scatter radiation produced and reaching the ir. In addition this chapter covers methods used to minimize the fog that this radiation causes on radiographs. Scatter radiation listen ska ter ray dee ay shun radiation that spreads out in different directions from a radiation beam when the beam interacts with a substance such as body tissue.
Unfortunately there is no ideal grid because all such devices absorb some primary radiation and allow some scattered radiation to pass through. Increased scatter radiation either produced within the patient or higher energy scatter exiting the patient affects the exposure to the patient and anyone within close proximity. The general design of a grid.
Use of protective curtains reduced the radiation dose to all medical staff members by shielding the entire operating room from scattered radiation and thus was very effective in reducing occupational radiation exposure. X rays that exit from the patient are remnant x rays and those that exit and interact with the image receptor are called image forming x rays. Scatter radiation occurs in three ways.
By definition scatter radiation occurs when radiation deflects off an object causing x rays to be scattered.
Scattered Radiation And Contrast
www.sprawls.org
 Radiographic Grids Image Production And Evaluation
Radiographic Grids Image Production And Evaluation
sites.google.com
 Scatter Radiation Exposure During Mobile X Ray Examinations
Scatter Radiation Exposure During Mobile X Ray Examinations
healthmanagement.org
 Angular Distribution Of Scattered Radiation Download Scientific
Angular Distribution Of Scattered Radiation Download Scientific
www.researchgate.net
 Scatter Radiation Exposure During Mobile X Ray Examinations
Scatter Radiation Exposure During Mobile X Ray Examinations
healthmanagement.org
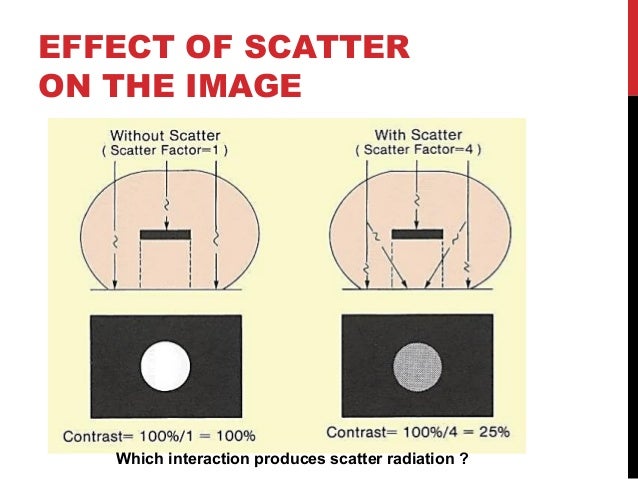 Rad 206 P11 Fundamentals Of Imaging Control Of Scatter Radiation
Rad 206 P11 Fundamentals Of Imaging Control Of Scatter Radiation
www.slideshare.net

www.scribd.com
 Pdf Modeling Of Scatter Radiation During Interventional X Ray
Pdf Modeling Of Scatter Radiation During Interventional X Ray
www.semanticscholar.org
0 Response to "All About Scatter Radiation"
Post a Comment