Black Body Radiation Britannica
The best practical blackbody is a small hole in a box with a blackened. Electromagnetic radiation electromagnetic radiation continuous spectra of electromagnetic radiation.
 Blackbody Radiation Physics Image And Video Britannica Com
Blackbody Radiation Physics Image And Video Britannica Com
www.britannica.com
Heat is the irregular motion of electrons atoms and molecules.
Black body radiation britannica. Since electrons are much lighter than atoms irregular thermal motion produces irregular oscillatory charge motion which. Stefan boltzmann law statement that the total radiant heat power emitted from a surface is proportional to the fourth power of its absolute temperatureformulated in 1879 by austrian physicist josef stefan as a result of his experimental studies the same law was derived in 1884 by austrian physicist ludwig boltzmann from thermodynamic considerations. The concept of such a perfect absorber of energy is extremely useful in the study of radiation phenomena.
Light blackbody radiation blackbody radiation refers to the spectrum of light emitted by any heated object. Blackbody in physics a surface that absorbs all radiant energy falling on it. Such spectra are emitted by any warm substance.
Room temperature objects about 300 k emit radiation with a peak. If e is the radiant heat energy emitted. Electromagnetic energy dw emitted per unit area and per second into a wavelength interval dl one angstrom by a blackbody at various temperatures between 3000 and 6000 k as a function of wavelengththe range of visible light is between the vertical dashed lines.
The spectral intensity of blackbody radiation peaks at a frequency that increases with the temperature of the emitting body. Black body radiation is the thermal electromagnetic radiation within or surrounding a body in thermodynamic equilibrium with its environment emitted by a black body an idealized opaque non reflective body. Plancks radiation law a mathematical relationship formulated in 1900 by german physicist max planck to explain the spectral energy distribution of radiation emitted by a blackbody a hypothetical body that completely absorbs all radiant energy falling upon it reaches some equilibrium temperature and then reemits that energy as quickly as it absorbs it.
The term arises because incident visible light will be absorbed rather than reflected and therefore the surface will appear black. It has a specific spectrum of wavelengths inversely related to intensity that depend only on the bodys temperature which is assumed. Common examples include the heating element of a toaster and the filament of a light bulb.
The higher the temperature the more rapid the motion.
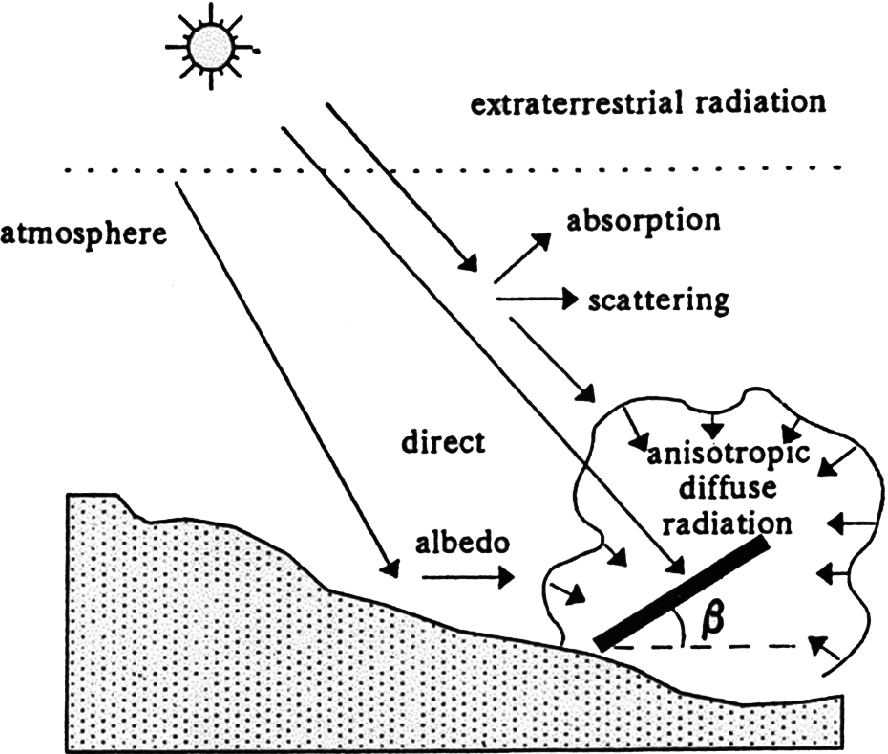 Solar Energy Springerlink
Solar Energy Springerlink
link.springer.com
 Max Planck Planck Cosmos
Max Planck Planck Cosmos
www.cosmos.esa.int
 What S Behind That Smile Using Analogies Facial Expressions And
What S Behind That Smile Using Analogies Facial Expressions And
bioone.org
 Physics The Science Of The Universe And Everything In It
Physics The Science Of The Universe And Everything In It
www.environmentalscience.org
 Spectroscopy For Industry Diamond Light Source Diamond
Spectroscopy For Industry Diamond Light Source Diamond
www.diamond.ac.uk
 Law Firm Sues Apple Samsung Claims Smartphones Exceed Rf
Law Firm Sues Apple Samsung Claims Smartphones Exceed Rf
macdailynews.com
 The Quantum Puzzle Ebook By Barry R Clarke 9789814696999
The Quantum Puzzle Ebook By Barry R Clarke 9789814696999
www.kobo.com
 The Britannica Guide To Relativity And Quantum Mechanics Physics Exp
The Britannica Guide To Relativity And Quantum Mechanics Physics Exp
www.slideshare.net
 The Encyclopaedia Britannica A Dictionary Of Arts Sciences
The Encyclopaedia Britannica A Dictionary Of Arts Sciences
www.alamy.com
0 Response to "Black Body Radiation Britannica"
Post a Comment